Jaw crushers reduce large rocks or ore by means of compression. Mechanical pressure is applied using the crusher’s two jaw; one is fixed while the other makes an eccentric movement. There are also primary and secondary types of these crushers. Jaw crushers are one of the most commonly preferred crushers due to their ability to crush all kinds of materials of any hardness, as well as their low-cost operation and easy maintenance.
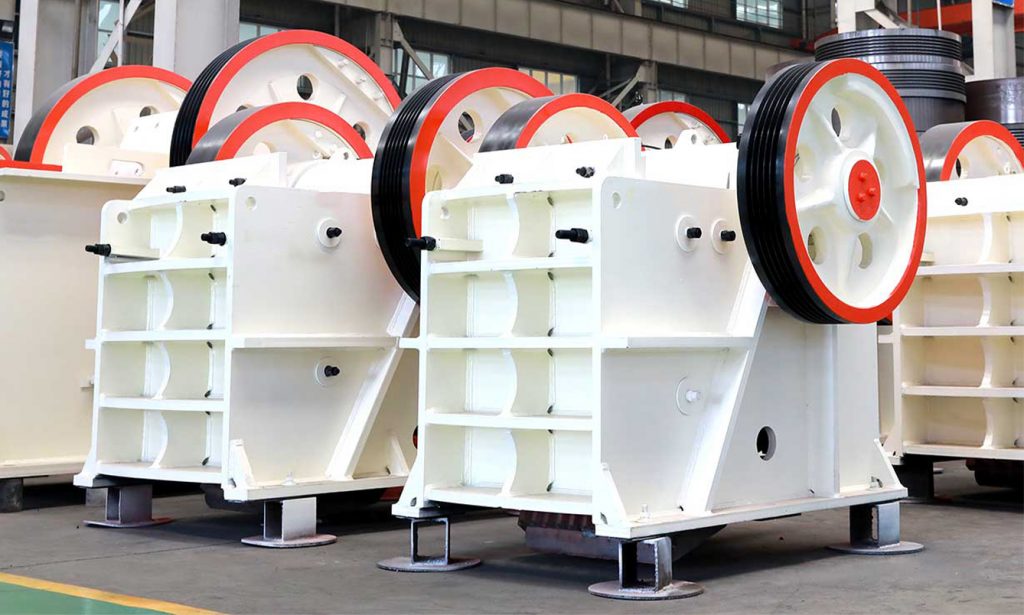

All in all, jaw crushers are convincing due to their rugged and reliable design with high capacities, low wear and tear and high ease of maintenance. The advantages can be summarized as follows:
When the jaw crusher is working, the movable jaw plate periodically reciprocates to the fixed jaw plate, sometimes approaching and sometimes leaving. When approaching, the material is crushed by extrusion, splitting and impact between the two jaw plates; when leaving, the crushed material is discharged from the discharge port by gravity.
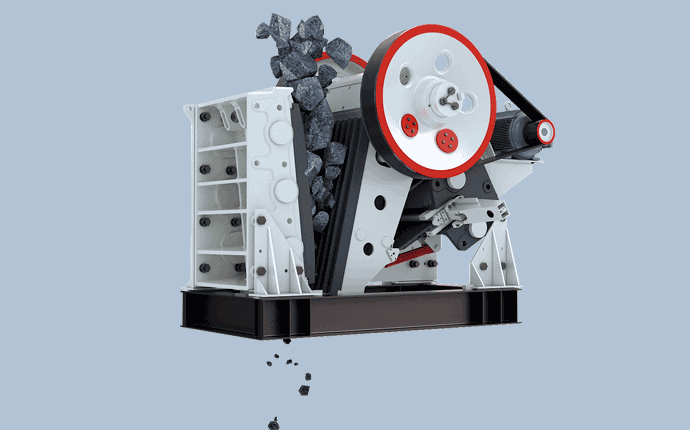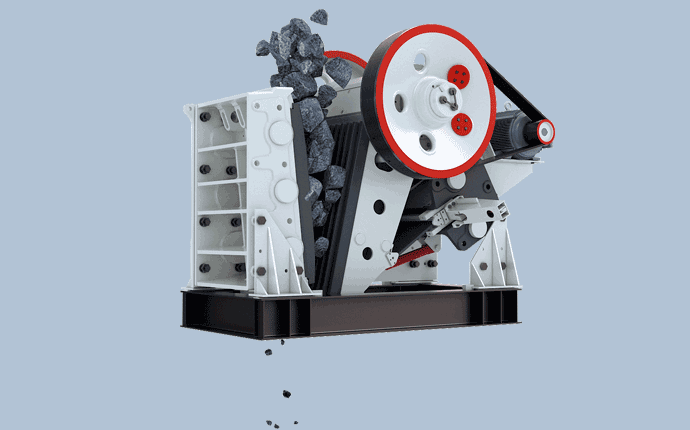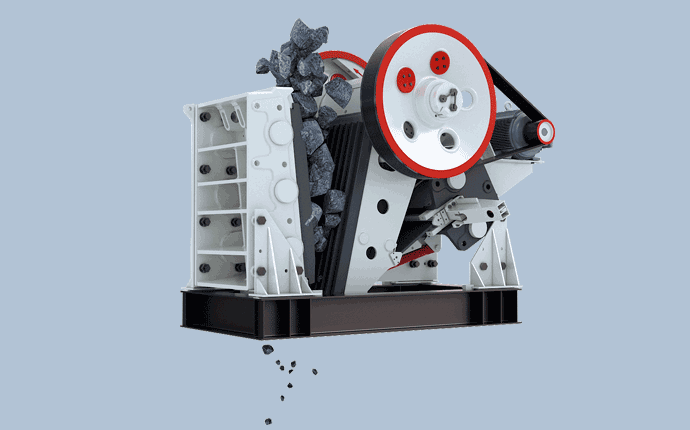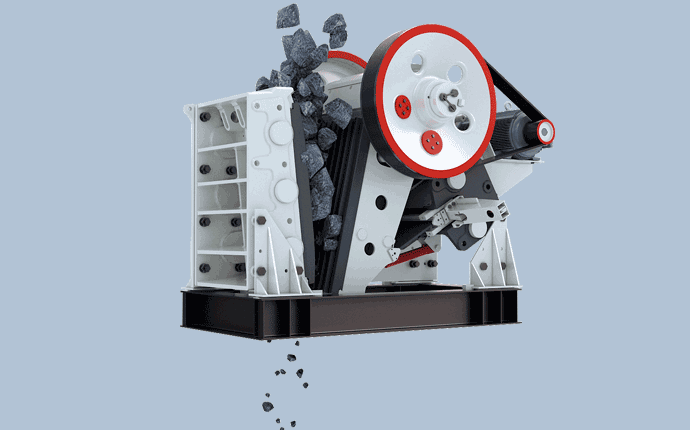
In the process of breaking huge rocks into smaller ones, the first crusher is usually the “main” crusher. The longest and most robust crusher is the jaw crusher. When feeding the jaw crusher, the material is poured into the crushing chamber containing jaw teeth from the top inlet, and the jaw teeth push the material against the chamber wall with great force, breaking it into smaller stones. Supporting the movement of the jaw teeth is an eccentric shaft that runs through the fuselage frame. Eccentric motion is usually produced by flywheels fixed at both ends of the shaft. Spherical roller bearings are often used in flywheels and eccentrically supported bearings, and the bearings must withstand huge shock loads, abrasive sewage and high temperatures.
| MJ 60 (Primary) |
MJ 65 (Primary) |
MJ 90 (Primary) |
MJ 110 (Primary) |
MJ 130 (Primary) |
MJS 90 (Secondary) |
MJS 110 (Secondary) |
|
| Feed Opening (mm) | 610×380 | 650×500 | 900×650 | 1100×850 | 1300×1000 | 900×200 | 1100×350 |
| CSS/min-max (mm) | 40-150 | 40-150 | 60-200 | 100-200 | 125-250 | 25-75 | 25-125 |
| Motor Power (kW) | 30 | 45 | 75 | 132 | 160 | 30 | 75 |
| Crusher Speed (rpm) | 330 | 330 | 293 | 228 | 210 | 330 | 330 |
| Capacity (mtph) | 20-110 | 30-120 | 50-250 | 100-300 | 275-600 | 20-110 | 110-220 |
| Weight (kg) | 6000 | 7000 | 11400 | 33000 | 43000 | 6000 | 11000 |
How much does it cost to buy equipment? Calculate the equipment investment budget immediately after making an appointment to leave a message, and more discounts are waiting for you.